- DAM coordinates the DES-BIOMETHANE project, which is in the final phase of its execution
- The research is framed within the parameters of circular economy, promoting waste management and utilization
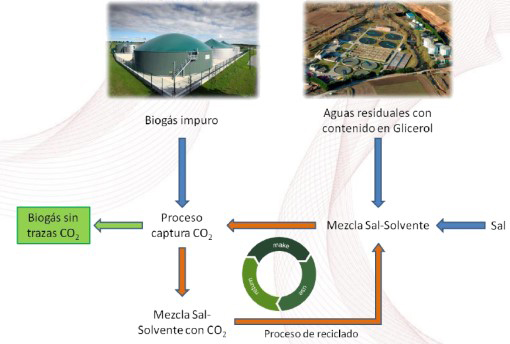
Produce low-cost biodegradable solvents known as “Deep Eutectic Solvents-DES”, taking advantage of waste generated in industrial effluents for biogas cleaning.
This is the main objective of the project entitled “Obtaining Deep Eutectic Solvents through recovery of industrial waste and its application in the purification of biogas obtained in WWTPs (DES-BIOMETHANE)”, coordinated by DAM (Depuración de Aguas del Mediterráneo), which is in the final phase of its development.
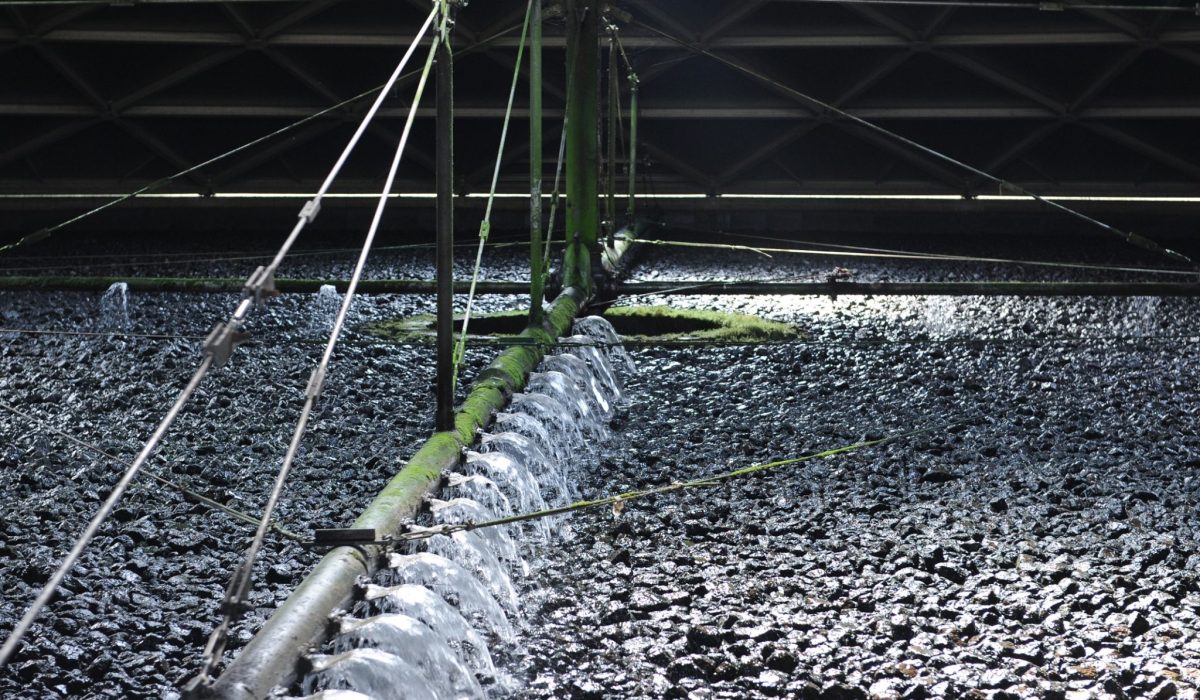
The research – in which Leitat also participates – starts from the reality that some WWTPs (Wastewater Treatment Plants) that have implemented the anaerobic digestion process for biogas production, use this biogas as a source of energy or heat. The capture or removal of CO2 by solvents has been proposed as an alternative to increase its yield.
“The study has developed a process to produce, through industrial waste, less polluting and more environmentally friendly solvents”
That is why the study has developed a process to produce, through industrial waste, less polluting and more environmentally friendly solvents and use them for biogas cleaning, as explained by the technical manager of the research from DAM, Javier Eduardo Sánchez.
“The project uses a component of industrial waste to produce a product capable of purifying the biogas that is produced in WWTPs, closing a cycle where a waste is reduced and CO2 emissions are minimized, giving added value to the generation of purer biogas,” says Dr. Sánchez.
The study, which has been running since November 2017, is part of the circular economy parameters that promote waste management and utilization.
According to the DAM researcher, there are many industrial wastes that can be used for the production of value-added by-products, “as we are demonstrating in this project, with the obtaining of biodegradable solvents that allow the purification or cleaning of biogas”.
Project execution status and results
During the study, the pre-treatment, separation, and purification of one of the components of the eutectic solvent were evaluated using the membrane distillation process.
Subsequently, the synthesis and characterization of the solvent obtained (DES) have been carried out. Finally, real and synthetic biogas tests were performed to assess the capacity for CO2 capture. The DES synthesized in this project is a biodegradable and low-toxicity solvent, which aligns with the principles of green chemistry.
“The results of the characterization made to the product show that it meets the physical and chemical characteristics of a eutectic solvent”
For now, the results of the characterization of the product show that it meets the physical and chemical characteristics of a eutectic solvent.
Likewise, the capacity for CO2 capture has been proven experimentally—through specific tests—and the operational variables that allow adequate adsorption and desorption of CO2, as well as the recovery or reuse of the solvent, have been studied.
At the moment, the project is in the final stage where the real behavior of the solvent using biogas is being evaluated.
Source: www.dam-aguas.es




